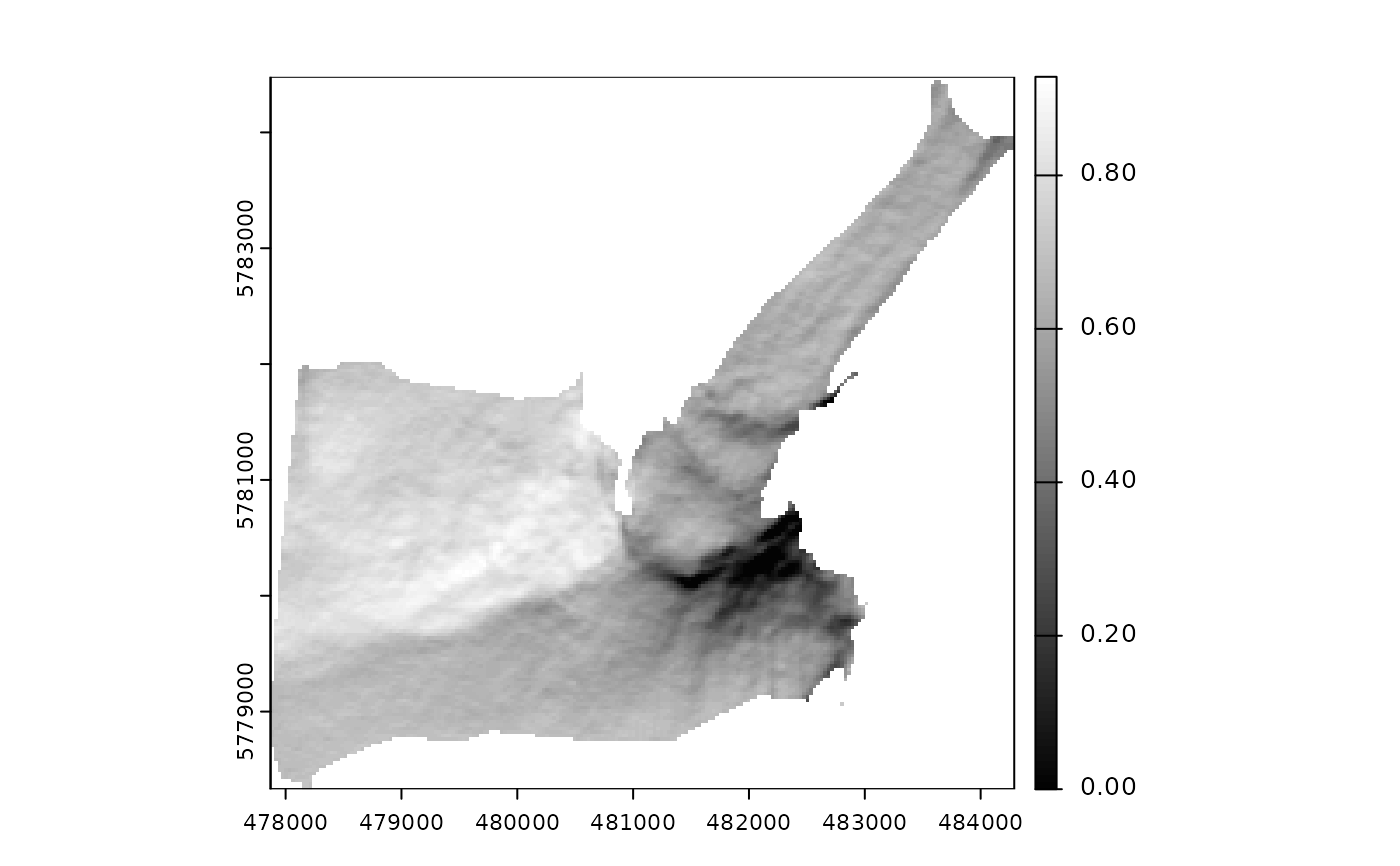
Computes the hypothetical illumination of a surface by setting the position of
the sun and calculating the illumination values for each grid cell of a DEM. The
hill_shade function is based upon the vectorial algebra algorithms developed
by Corripio (2003)
. This function has been
optimized and updated to take advantage of the infrastructure provided by the terra package.
References
Corripio JG (2003). “Vectorial algebra algorithms for calculating terrain parameters from DEMs and solar radiation modelling in mountainous terrain.” International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 17(1), 1–23. doi:10.1080/713811744 .